Heart Involvement in Hemoglobinopathies: Two Case Reports and Brief Review of Literature
Wael Yaakoubi*, Manel Ben Hlima, Sana Ouali, Fathia Mghaith and Med Sami Mourali
Wael Yaakoubi*, Manel Ben Hlima, Sana Ouali, Fathia Mghaith and Med Sami Mourali
Department of Cardiology, La Rabita Hospital Ministry of Public Health, Tunis, Tunisia
- *Corresponding Author:
- Wael Yaakoubi
Department of Cardiology, La Rabita Hospital Ministry of Public Health, Tunis, Tunisia
E-mail:yaakoubiwael@gmail.com
Received date: 03 January, 2022, Manuscript No. IPMCRS-22-12524; Editor assigned date: 05 January, 2022, PreQC No. IPMCRS-22-12524(PQ);Reviewed date: 17 January, 2022, QC No IPMCRS-22-12524; Revised date: 24 January, 2022, Manuscript No. IPMCRS-22-12524(R);Published date: 31 January, 2022, DOI: 10.36648/2471-8041.8.2.211
Citation: Yaakoubi W, Hlima MB, Ouali S, Mghaith F, Mourali MS (2021). Heart Involvement in Hemoglobinopathies: Two Case Reports and Brief Review of Literature. Med Case Rep Vol.8 No.2:211
Abstract
Τhe two main determinants of cardiovascular phenotype in haemoglobinopathy patients are the underlying molecular defect responsible for the main disease and the therapy applied for its management. The spectrum of cardiovascular manifestations in haemoglobinopathies is wide and includes ventricular dysfunction, pulmonary hypertension, thromboembolic events.
We report a case of thalassemia and one of sickle cell disease having different clinic phenotype with brief literature review.
Keywords
Heart failure; Hemoglobinopathies; Mortality
Background
Hereditary haemoglobin disorders, also termed haemoglobinopathies, include mainly beta-thalassemia and sickle cell disease and represent the most common monogenic disorders in human. Cardiac complications are still a leading cause of mortality and morbidity in patients with haemoglobinopathy, have dramatically reduced in patient populations receiving modern regular therapy and follow-up.
Case One
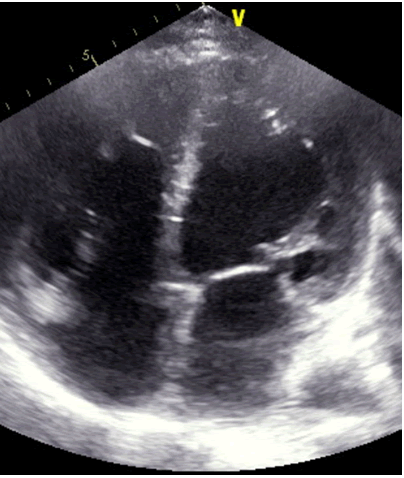
A patient 32-year-old male who was receiving periodic transfusions with intermittent chelation therapy for Cooley's anaemia came to our clinic with complaint of Dyspnoea on Exertion (DOE) in the past two years. The patient was followed up at the haematology department. He had a splenectomy at three years old. On the physical examination the patient had a global heart failure chart, high abundance ascites and hepatomegaly. He was in rapid atrial fibrillation. After treatment of congestion and slowing atrial fibrillation, the patient was explored by an echocardiography. Severe LV systolic dysfunction with a LVEF of about 20%; mitral regurgitation up to moderate degree was observed (Figure 1). The right ventricle is very dilated with massive and laminar tricuspid insufficiency due to lack of coaptation of the cusps thus creating a tricuspid hiatus. A restrictive filling pattern in both ventricles with both ventricular systolic dysfunctions were evident in this patient, also a lower right ventricular function: Free wall TDI peak systolic velocity was 7 cm/sec. The patient was probed by MRI revealing advanced hepatic and cardiac hemochromatosis. Endocrine pancreas is also reached in view of high glycaemic dosage relating to secondary diabetes. Our patient died while in hospital because he had an electrical storm.
Case Two
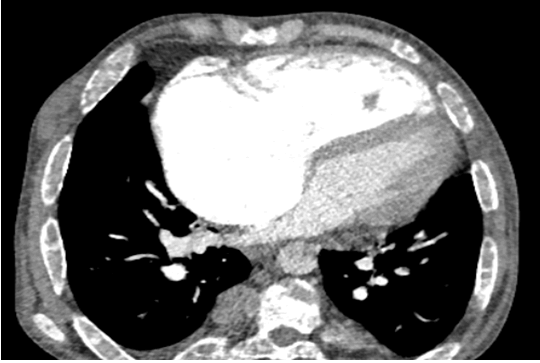
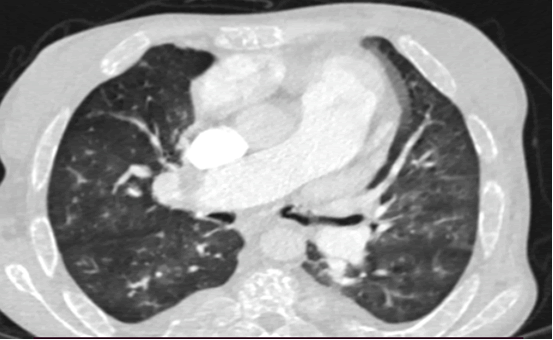
A patient 28-year-old male who was receiving periodic transfusions with intermittent chelation therapy for Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) came to our clinic with complaint of Dyspnoea on Exertion (DOE) in the past two years. The patient was followed up at the haematology department, she was on fold in, hydrea and vitamin C. On the physical examination the patient had only an enlarged jugular vein, high abundance ascites and hepatomegaly. At the electrocardiogram revealed a regular rhythm and a complete right bundle brunch block. At echocardiography, LVEF was about 60%. The right ventricle is very dilated (Figure 2) with massive tricuspid insufficiency due to a diastasis in tricuspid valve. A lower right ventricular function: Free wall TDI peak systolic velocity was 4 cm/sec. Estimation of systolic pulmonary artery pressure from tricuspid insufficiency was about 120 mmHg which was very high and supra-systemic. The patient was explored by cardiac CT-scan revealing advanced pulmonary hemochromatosis (Figure 3), no pulmonary emboli and very enlarged right cardiac cavities. Our patient died of acute chest syndrome during hospitalization.
Discussion
Thalassemia heart disease involves mainly left ventricular dysfunction caused by transfusion-induced iron overload [1]. In addition to the left ventricular abnormalities right ventricular dysfunction represents a common, yet less well explored complication in the cardiopulmonary spectrum of the disease. Biventricular dilated cardiomyopathy is still considered as the leading cause of mortality in patients with betathalassemia major [2]. In B-Thalassemia, the defect in haemoglobin is quantitative, characterized by a reduction or total depletion of ïÿýïÿý chain synthesis, and the severity of chain deficiency determines the clinical phenotype, which extends from the severe and transfusion-dependent thalassaemia major to the milder and often transfusion-independent thalassaemia intermedia. The heart takes up physiologic amounts of iron through transferrin receptors, but this process is tightly regulated and does not lead to iron overload. When transferrin-binding capacity is exceeded, circulating low molecular weight Non-Transferrin-Bound Iron (NTBI) species appear. NTBI is oxidatively active and can enter through nonspecific, poor-regulated cation channels in the heart, leading to cardiac iron overload [3]. Pulmonary Hypertension (PH) in thalassemia is associated with vasoconstriction, vascular smooth muscle proliferation and irregular endothelium in pulmonary arteries with associated thrombosis. These conditions all contribute to luminal narrowing and eventual right ventricular failure. It includes plexiform and concentric medial hyperplastic pulmonary vascular lesions, and in situ pulmonary artery thrombosis [4]. These pulmonary vascular abnormalities may have resulted from chronic embolic disease in other patients. Advancing age and a history of splenectomy are major risk factors for PH in this population [5,6]. Another phenomena can explains this phenomena as the process of haemolysis disables the arginine-nitric oxide pathway through the simultaneous release of erythrocyte arginase and cell-free haemoglobin. Both nitric oxide and its obligate substrate arginine are rapidly consumed .Outcome of heart failure, in advanced cardiac iron overload states, is dismal [7-9]. Compared to reported 3-month mortality rate of 58% in the pre-chelation era, recent findings indicate an improved prognosis over older series. Five-year survival was 48% and positively associated with left ventricular systolic function. All deaths occurred among patients with biventricular cardiomyopathy, shortly after involvement. Such improved survival is explained by the widespread use of chelation treatment and possibly also by better management of anaemia and use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Although LV iron overload cardiomyopathy is a leading cause of death in patients with thalassaemia major this complication appears to be uncommon in SCD patients. Left ventricular dysfunction due to sickle cell disease is rare. In SCD, the defect in haemoglobin is qualitative, as a substitution at the sixth amino acid residue in the ïÿýïÿý chain results in synthesis of an abnormal haemoglobin, termed haemoglobin S, instead of the normal haemoglobin A [10]. Left ventricular systolic dysfunction is uncommon in patients with SCD: A meta-analysis of 19 controlled case studies has shown similar LV Ejection Fraction (LVEF) in homozygous S patients compared to healthy controls [11]. Accordingly, the prevalence of an LVEF <50% is low, ranging from 0% to 2.5% in ultrasound cohorts studies and 0% to 4% in smaller CMR studies [12,13]. SCD-related PH involves several mechanisms. First, as pulmonary pressure is the product of flow and pulmonary vascular resistances, high cardiac output in SCD induces elevated pulmonary pressure whether pulmonary vascular resistances are altered or not [14,15]. Second, chronic volume overload might lead to LV failure and subsequent pulmonary venous hypertension [16]. Third, intravascular haemolysis could induce pulmonary arterial vasculopathy mainly driven by nitric oxide scavenging due to free plasma haemoglobin [17,18]. Finally, several other mechanisms may participate including, chronic hypoxaemia, post-embolic PH, SCD-related lung injury, chronic liver disease and asplenia.
In SCD, the pulmonary vascular bed is commonly affected. Pneumonia may be difficult to distinguish from pulmonary infarction and both may coexist. Intravascular sickling may cause pulmonary vascular occlusion in the absence of radiologic changes and in some patients bone marrow and fat released from infarcted bone may embolize to the lungs [19]. In the autopsy series of Gerry et al. 30% of adults and 22% of children had right ventricular hypertrophy. Three of these patients had had right ventricular failure, considered to be due to cor pulmonale [20].
Conclusion
The main cardiac involvement during major beta thalassemia is left ventricular dysfunction or in extreme cases biventricular dilated cardiomyopathy on the other hand sickle cell disease mainly causes right ventricular dilatation and dysfunction secondary to sickle cell lung pathology. A major near-term issue to address is the establishment of criteria for early disease-specific treatment of patients with MBT and SCD to avoid cardiovascular complications.
References
- Grisaru D, Rachmilewitz EA, Mosseri M, Gotsman M, Lafair JS,et al. (1990) Cardiopulmonary assessment in beta-thalassemia major. Chest 98: 1138âÃâ¬Ãâ42.
[Cross Ref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Levy RI, Moskowitz J. (1982) Cardiovascular research: decades of progress, a decade of promise. Science 217: 121âÃâ¬Ãâ9.
[Cross Ref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Rund D, Rachmilewitz E. (2005) Beta-thalassemia. N Engl J Med 353: 1135âÃâ¬Ãâ46.
- Wood JC. (2009) Cardiac complications in thalassemia major. Hemoglobin 33 Suppl 1:S81-S86.
[Cross Ref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Morris CR, Gladwin MT, Kato GJ (2008) Nitric oxide and arginine dysregulation: a novel pathway to pulmonary hypertension in hemolytic disorders. Curr Mol Med 8: 620âÃâ¬Ãâ32.
[Cross Ref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Atichartakarn V, Likittanasombat K, Chuncharunee S, Chandanamattha P, Worapongpaiboon S, et al. (2003) Pulmonary arterial hypertension in previously splenectomized patients with beta-thalassemic disorders. Int J Hematol 78: 139âÃâ¬Ãâ45.
[Cross Ref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Phrommintikul A, Sukonthasarn A, Kanjanavanit R, Nawarawong W. (2006) Splenectomy: a strong risk factor for pulmonary hypertension in patients with thalassaemia. Heart Br Card Soc 92: 1467âÃâ¬Ãâ1472.
[Cross Ref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Engle MA, Erlandson M, Smith CH. (1964) Late Cardiac Complications Of Chronic, Severe, Refractory Anemia With Hemochromatosis. Circulation 30: 698âÃâ¬Ãâ705.
[Cross Ref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Engle MA. (1969) Cardiac involvement in Cooley's anemia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 119: 694–702.
[Cross Ref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Felker GM, Thompson RE, Hare JM, Hruban RH, Clemetson DH et al. (2003) Underlying causes and long-term survival in patients with initially unexplained cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 342: 1077–1084.
[Cross Ref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Rees DC, Williams TN, Gladwin MT. (2010) Sickle-cell disease. The Lancet. 376: 2018âÃâ¬Ãâ2031.
[Cross Ref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Poludasu S, Ramkissoon K, Salciccioli L, Kamran H, Lazar JM. (2013) Left ventricular systolic function in sickle cell anemia: a meta-analysis. J Card Fail. 19: 333âÃâ¬Ãâ341.
[Cross Ref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Desai AA, Patel AR, Ahmad H, Groth JV, Thiruvoipati T et al. (2014) Mechanistic Insights and Characterization of Sickle Cell Disease Associated Cardiomyopathy. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 7: 430âÃâ¬Ãâ7.
[Cross Ref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Wood JC, Tyszka JM, Carson S, Nelson MD, Coates TD. (2004) Myocardial iron loading in transfusion-dependent thalassemia and sickle cell disease. Blood. 103: 1934âÃâ¬Ãâ6.
[Cross Ref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Mushemi-Blake S, Melikian N, Drasar E, Bhan A, Lunt A et al. (2015) Pulmonary Haemodynamics in Sickle Cell Disease Are Driven Predominantly by a High-Output State Rather Than Elevated Pulmonary Vascular Resistance: A Prospective 3-Dimensional Echocardiography/Doppler Study. Connes P éditeur. PLOS ONE. 10: e0135472.
[Cross Ref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Caughey MC, Hinderliter AL, Jones SK, Shah SP, Ataga KI. (2012) Hemodynamic Characteristics and Predictors of Pulmonary Hypertension in Patients with Sickle Cell Disease. Am J Cardiol. 109: 1353âÃâ¬Ãâ7.
[Cross Ref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Junqueira FP, Fernandes JL, Cunha GM, T A Kubo T, M A O Lima C et al. (2013) Right and left ventricular function and myocardial scarring in adult patients with sickle cell disease: a comprehensive magnetic resonance assessment of hepatic and myocardial iron overload. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 15: 83.
[Cross Ref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Fonseca GHH, Souza R, Salemi VMC, Jardim CVP, Gualandro SFM. (2012) Pulmonary hypertension diagnosed by right heart catheterisation in sickle cell disease. Eur Respir J 39: 112âÃâ¬Ãâ8.
[Cross Ref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Farmakis D, Aessopos A.(2011) Pulmonary Hypertension Associated With Hemoglobinopathies: Prevalent But Overlooked. Circulation. 123: 1227âÃâ¬Ãâ32.
[Cross Ref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Baroldi G (1969) High resistance of the human myocardium to shock and red blood cell aggregation (sludge). Cardiology 54: 271âÃâ¬Ãâ277.
[Cross Ref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
- Gerry JL, Bulkley BH, Hutchins GM (1978) Clinicopathologic analysis of cardiac dysfunction in 52 patients with sickle cell anemia. Am J Cardiol 42: 211âÃâ¬Ãâ216.
[Cross Ref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]

Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences